Exportation
The production of sugar has advanced rapidly in the modern era, and slave labor has been replaced by technology. For many years, Brazil has led the way in the development of the sugar industry. It has sequenced the genome of sugar cane, created over 100 strains of the crop, and developed methods for milling and refining the crop that are so sophisticated that refineries and mills can often sell excess energy back to the national grid instead of needing to pay for electricity to run their operations.
Brazil was also the inventor of VHP raw sugar, a raw sugar product with a minimum sucrose content of 99.4% . Prior to the invention of VHP raw sugar, raw cane juice would be boiled or evaporated until all that was left was a dark brown natural sugar product full of contaminants and mixed with molasses. This raw sugar required a great deal of processing to refine it into the sparkling white ICUMSA 45 sugar which has gained dominion throughout most of the developed world as a sweetener of choice.
To make VHP sugar, raw cane juice is heated to a boiling point where the concentration is high enough to cause sucrose crystals to form. The juice is then allowed to cool until the crystals do form, and both the solution and the crystals are separated by centrifuging. The crystals are separated from the residual liquid content—molasses—by the centrifugal process.


We export in bulk, break bulk, and containerized forms.
Vessels:
Sugar in containers 20 Icumsa 45 – 100 – 150 Max. 26 m/tons package: Polybags 50 kilos 520 polybags per unit
Sugar Icumsa 45 – 100 and 150
In Break Bulk vessel
Package: polybags 50 kilos
Vessel Qty:
12.500 m/tons
25.000 m/tons
50.000 m/tons
Raw sugar – Icumsa 800 – 1200
Bulk cargo
Only in bulk vessel
Vessel Qty:
12.500 m/tons
25.000 m/tons
50.000 m/tons
Raw sugar in containers 20
Only in big bags 1 m/ton or 2 m/tons
Max. weight 20 m/tons with 20 big bags per unit
** N.B – Prices C&F or CIF depending on quantity and destination. **
Procedure:
- Buyer issues ICPO and BCL (ICPO endorsed by bank officer)
- Seller approves ICPO and sends the Draft Contract
- Buyer / Seller sign the Contract
- Buyer opens non-operative SBLC or MT 103 to seller bank
- Seller issues POP to turn operative the financial instrument
- Shipments start as per contract terms.
Our Methods & Technology for Manufacturing Sugar
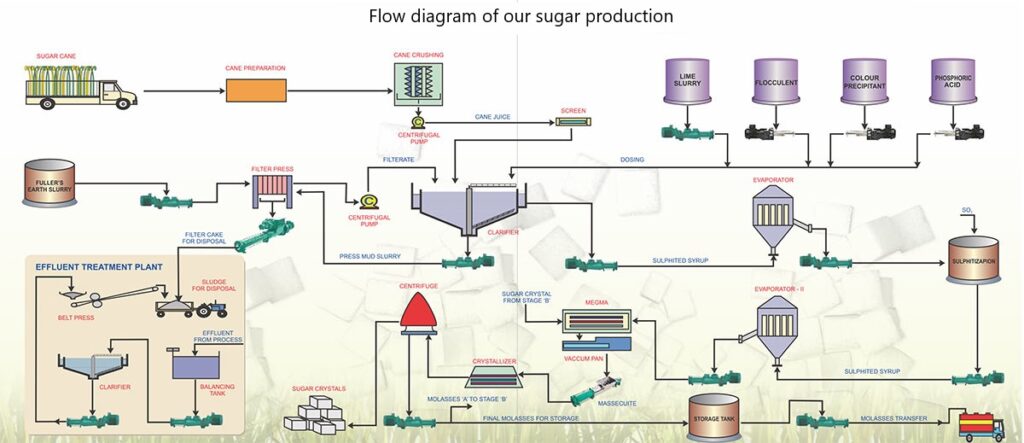
A naturally occurring carbohydrate, sugar (sucrose) is found in all fruits and vegetables. It is a significant byproduct of photosynthesis, the process through which plants convert solar energy into nourishment. The highest concentrations of sugar are found in sugarcane and sugar beets, from which it is extracted for industrial usage. Refining is the process of removing the natural sugar that is contained in the cane stalk or beet root from the remaining plant material.
For sugarcane, the process of refining is carried out in the following steps:
- Pressing of sugarcane to extract the juice
- Boiling the juice until it begins to thicken and sugar begins to crystallize.
- Spinning the crystals in a centrifuge to remove the syrup, producing raw sugar.
- Shipping the raw sugar to a refinery where it is washed and filtered to remove remaining non-sugar ingredients and color.
- Crystallizing, drying, and packaging the refined sugar.
Processing beet sugar is similar, except it is done all at once without the need for raw sugar. To extract the juice that contains sugar from the beet fiber, sugar beets are cleaned, cut into slices, and immersed in hot water. The juice, which is high in sugar, is further processed similarly to cane sugar, including purification, filtering, concentration, and drying.
The concept of capacity utilization for the sugar industry differs conceptually from that of other industries. The amount of sugarcane crushed in a given day, the recovery rate—which is mostly determined by the cane’s quality—and the duration of the crushing season are the three main determinants of the outcome.
Cane is not transported very far, therefore a factory’s ability to manage the quality of the cane it receives is limited by its geographic position. The location also affects how long the crushing season lasts.
Granulated sugar is simply pure sucrose crystals. Based on the size of the crystals, sugar can be divided into seven categories. Professional bakers and food processors are the only ones who use the majority of these. Because each crystal size offers distinct functional qualities, the sugar is suitable for the particular requirements of the food processor.
